What is Chronic Venous Insufficiency?
Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI) is a medical condition characterized by the inadequate flow of blood through the veins, primarily in the lower extremities. This insufficiency typically arises when the one-way valves within the veins fail to function properly, leading to a reversal of blood flow. As a result, blood tends to pool in the legs, thereby increasing venous pressure. CVI is not merely a cosmetic issue, as it can result in a range of complications if left unaddressed, including skin changes, ulcers, and infections.
The significance of understanding CVI lies in its prevalence among populations. It is estimated that approximately 20-25% of adults in the United States may experience some form of venous insufficiency during their lifetime. Notably, CVI is more common in individuals over the age of 50, though younger individuals can also be affected. Risk factors for developing this condition include obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, prolonged standing or sitting, and a family history of venous disorders. Moreover, conditions such as pregnancy can further exacerbate the likelihood of developing CVI due to increased pressure on the veins.
If ignored, chronic venous insufficiency can lead to a series of complications that may significantly impair an individual’s quality of life. These complications may range from superficial skin changes, like varicose veins, to more severe issues such as venous ulcers and even deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Thus, early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial to mitigate these adverse effects. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the functional limitations caused by CVI will not only enrich patients’ knowledge but also foster timely intervention and treatment options.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a condition that occurs when the veins in the legs fail to efficiently return blood to the heart. The symptoms associated with this ailment can significantly disrupt daily life and, if left untreated, may lead to more severe health complications. Common indicators of CVI include swollen legs, persistent aching or heaviness in the limbs, the presence of varicose veins, and noticeable skin changes such as discoloration or ulcerations.
Swelling, or edema, is among the most prevalent symptoms and often occurs after prolonged standing or sitting. This builds pressure in the veins and results in fluid leakage into surrounding tissues. Patients may report a feeling of heaviness or achiness in their legs, along with fatigue, particularly after physical activities or long periods of inactivity. Varicose veins, characterized by dilated and twisted veins, are another visible symptom that can lead to both cosmetic concerns and discomfort. In advanced cases, skin changes may manifest, including a change in color around the ankles, itching, and the development of leg ulcers due to impaired blood flow.
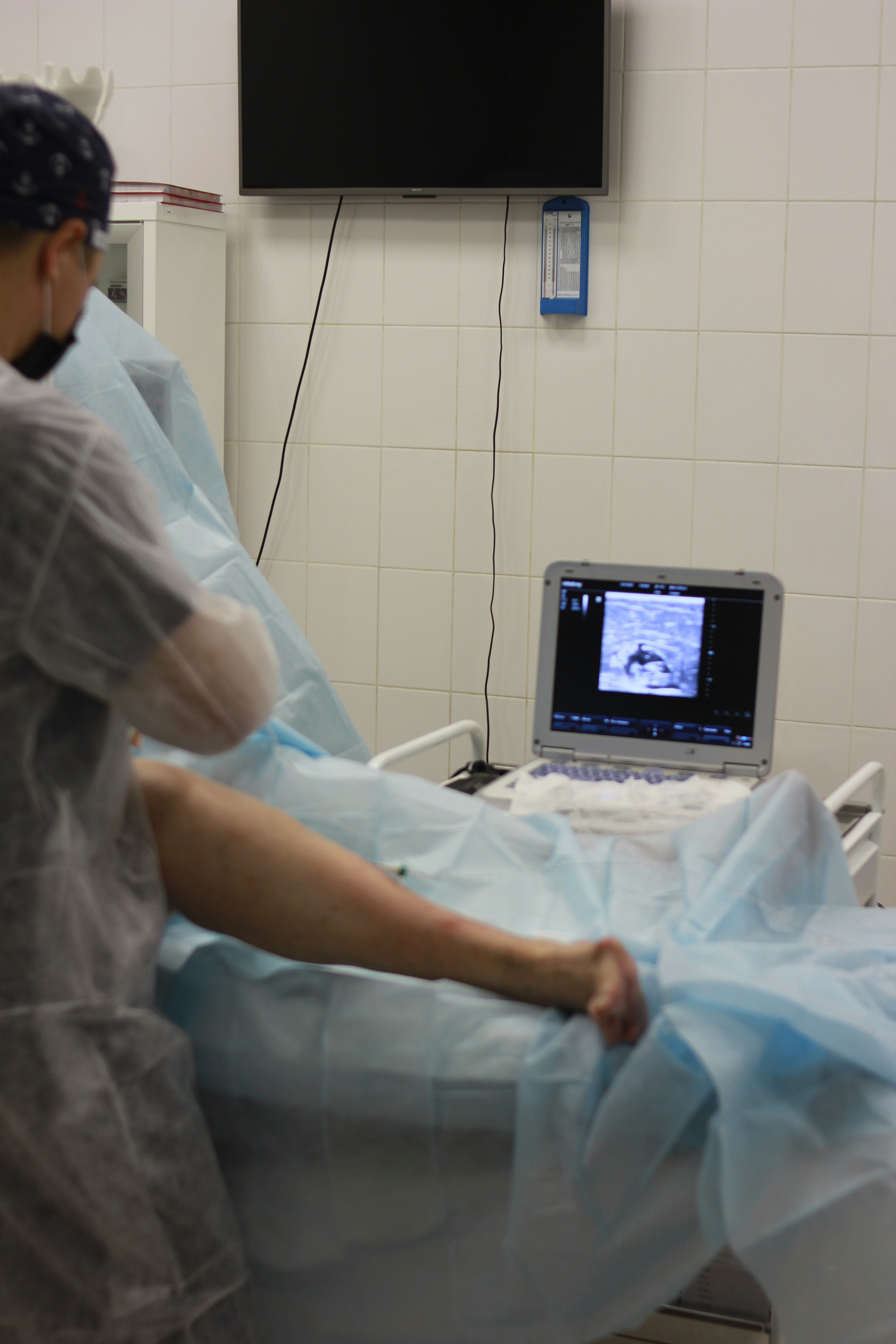
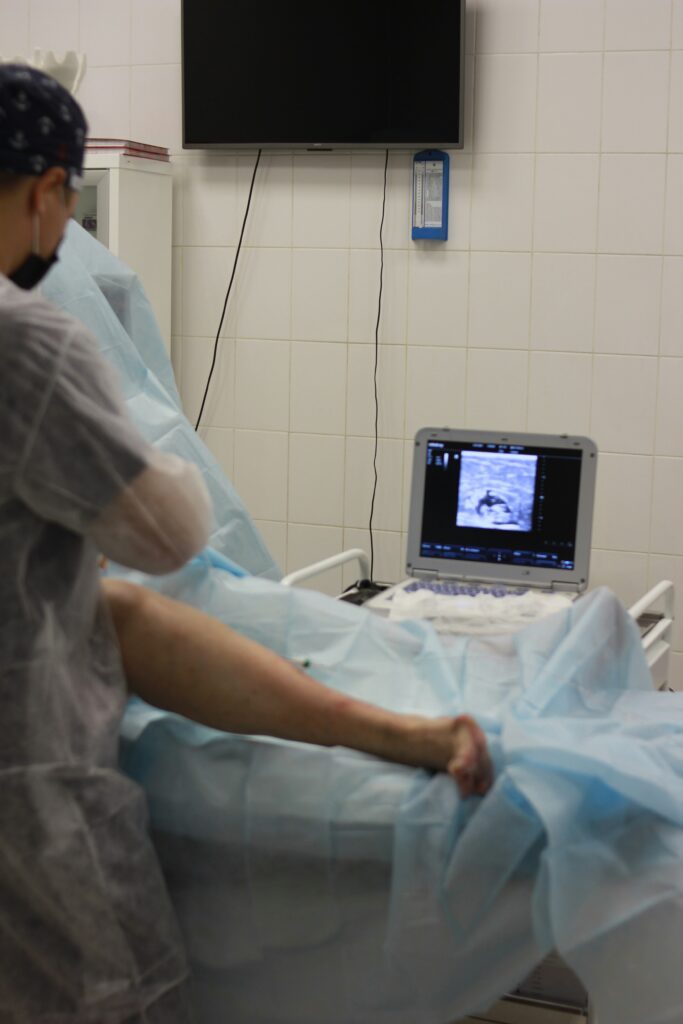
Diagnosing chronic venous insufficiency typically involves a thorough clinical evaluation, starting with a detailed discussion of symptoms and medical history. Healthcare professionals will perform a physical examination, assessing the veins and any swelling present in the legs. To confirm the diagnosis or evaluate the severity of the condition, imaging tests such as duplex ultrasound may be employed. This non-invasive procedure helps visualize blood flow in the veins and identifies any abnormal patterns, providing a clearer picture of venous function. Early diagnosis is crucial, as it allows for timely intervention and can prevent the escalation of CVI-related complications.
Treatment Options for Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) presents a range of challenges and discomfort for those affected, necessitating a comprehensive approach to treatment. Managing CVI involves both conservative and invasive treatments tailored to fit individual patient needs. The first line of defense often includes lifestyle modifications such as weight management, increased physical activity, and elevating the legs to improve venous circulation. These adjustments can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals with CVI.
Alongside lifestyle changes, compression therapy plays a crucial role in the treatment landscape. This involves wearing graduated compression stockings, which help to maintain venous pressure and prevent blood from pooling in the veins. Compression therapy is generally well-tolerated and can be effective in reducing symptoms like swelling and discomfort. However, it requires consistent use for maximum benefit.
Medications may also be prescribed to address specific symptoms associated with chronic venous insufficiency. These can include anticoagulants to prevent blood clots or medications that help alleviate pain and swelling. It is important to consult a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate pharmacological options, as individual responses can vary.
For patients who do not experience sufficient improvement with conservative treatments, minimally invasive procedures such as endovenous laser therapy (EVLT) and sclerotherapy offer advanced alternatives. These techniques aim to close off problematic veins while allowing blood to reroute through healthier vessels. Although these procedures have a shorter recovery time and fewer complications compared to traditional surgery, they may not be suitable for everyone.
In some cases, surgical interventions, such as vein ligation or vein stripping, are considered. While these options can provide significant relief, they come with inherent risks and longer recovery periods. Thus, clinical decisions should be made collaboratively between patients and healthcare providers, ensuring that each treatment plan aligns with the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall health profile.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, but several strategies can be implemented to help prevent its development and manage its symptoms effectively. One of the primary preventive measures is maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This includes adhering to a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Such dietary choices can enhance vascular health and facilitate effective blood circulation, reducing the risk of venous insufficiency.
Regular exercise plays a crucial role in the prevention and management of chronic venous insufficiency. Engaging in activities that promote leg strength and circulation, such as walking, swimming, and cycling, can help alleviate symptoms by encouraging blood flow in the veins. It is advisable to incorporate 30 minutes of moderate exercise into one’s daily routine. Additionally, weight management is essential, as excess body weight can place additional pressure on the veins in the legs, exacerbating the risk of developing CVI.
Wearing compression garments can also aid in managing symptoms associated with chronic venous insufficiency. These garments, which include compression stockings or sleeves, exert outward pressure on the legs, thereby improving venous blood flow and reducing swelling. For individuals already diagnosed with CVI, it is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate level of compression required.
Routine monitoring of symptoms is essential to managing chronic venous insufficiency effectively. Individuals should remain vigilant for any signs of worsening conditions, such as increased swelling, skin changes, or ulcers. Seeking prompt medical advice upon noticing such changes can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with CVI. Furthermore, regular check-ups with healthcare providers can assist in managing existing conditions and modifying treatment plans as necessary.